Dragonchain Solves the Blockchain Trilemma
From the beginning, blockchain development has been challenged to create a blockchain that can scale while remaining decentralized and secure. Otherwise known as the blockchain trilemma, the prevailing thought is that achieving all three is difficult and some even say an impossible task. The term blockchain trilemma dates as far back as 2016 and is largely attributed to Vitalik Buterin. In a recent blog, Buterin addresses the trilemma as a scalability challenge and advocates for a sharding solution for Ethereum. We won’t get into Buterin’s sharding solution except to say that it too has pros and cons, as stated in the aforementioned blog.
Blockchain developers are often forced to make trade-offs that prevent them from achieving scalability, security, and decentralization. Before we get into how Dragonchain approaches all three aspects of blockchain development, let’s first familiarize ourselves with the terms.
Security
Typically security refers to the ability of the blockchain system to defend against both internal and external attacks and system failures. Often thought of in terms of the blockchain source code, the open-source software that lays the foundation of each blockchain is a sought-after target for nefarious actors. A blockchain must employ measures that prevent the validation of fraudulent transactions and protect against the well-known 51% attack. Security should lay the foundation of any blockchain and should be the first thought for businesses. Without security measures in place, data is vulnerable to corruption, making decentralization and scalability useless.
Scalability
Generally, scalability references the number of transactions a blockchain can process without slowing down or becoming too costly. The scalability of a blockchain is often compared to traditional financial services like Visa. Blockchains should be able to settle unpredictably large numbers of transactions at a minimal cost in order to make mass adoption possible. If a blockchain cannot process business data at volume, then the blockchain will never see adoption numbers to rival traditional systems.
Decentralization
Decentralization refers to a blockchain system not controlled by a central entity. Verification nodes are disparate and span the globe where anyone can validate blocks from anywhere in the world. In a typical blockchain, every node in the system will run the same blockchain and has access to the same information.
Businesses don’t typically look for decentralization when accessing blockchain networks. In fact, due to data privacy concerns and regulations such as HIPAA, CCPA, and GDPR, businesses can often not use a fully decentralized network. Many classes of business information are too sensitive to allow any level of exposure even with obfuscation or encryption. Decentralization however is not an all-or-nothing question. That is, certain aspects of a blockchain solution can be decentralized while others remain centralized.
Addressing the Trilemma in the Real World
As mentioned, simultaneously maximizing decentralization, scalability, and security is a difficult task. For example, the most recognizable proof of work (PoW) system, Bitcoin, is fully decentralized and extremely secure, but it does not scale and is prohibitively slow for mass adoption. Proof of stake (PoS) systems, in theory, can scale better than Bitcoin but the most scalable are often purely centralized and as such are not fundamentally secure.
Blockchain developers are still trying to find the correct balance of security, scalability, and decentralization. However, the Dragonchain platform has had the blockchain trilemma considered and solved since 2014. The three aspects are so intertwined into the foundation of the platform that it is difficult to separate the three. But let’s try.
Dragonchain’s Blockchain Security
Data exposure and security are known issues for large institutions wanting to leverage blockchain technology, yet for most blockchains, security is an afterthought. Protection of business data is and always has been a primary objective for the Dragonchain platform. Beyond the typical IT security features and best practices, Dragonchain offers many alternatives and advanced capabilities to counter security threats using traditional IT tools and best practices.
For most blockchains, security is an afterthought.
Blockchain Architectures
There are generally three types of blockchain architectures; private, public, and hybrid.
Public Blockchains Architecture
Public or permissionless blockchains allow anyone to participate. These systems are fully decentralized and transparent where anyone can examine transaction details and smart contract logic. People gravitate toward public blockchains as their decentralization makes them highly censorship-resistant and extremely hard for authorities to shut down. However, public blockchains do present security concerns that are particularly limiting for businesses.
Often overlooked, the sole use of public blockchains is the equivalent of placing your operational system, including proprietary data and smart contracts, in the public domain risking exposure of sensitive data and business logic. Additionally, public blockchains do not allow businesses to adhere to CCPA, GDPR, or HIPAA regulations.
Private Blockchain Architecture
Private or permissioned blockchains are useful for businesses that want to collaborate and share information but don’t want their sensitive business data exposed on a public blockchain. Transactions on a permissioned blockchain are private and are only available to ecosystem participants that have been permitted to join the network. These chains are centralized and as such the entities running private blockchains have significant control over participation and governance structures. Unfortunately, private closed systems do not offer transparency and make it hard to share data across networks.
Hybrid Blockchain Architecture
A hybrid system combines the privacy benefits of a private blockchain with the security and transparency benefits of a public blockchain. Coupled with Dragonchain’s patented Interchain technology, our hybrid blockchain architecture leverages multiple blockchains to seamlessly connect data between any two systems to allow users to selectively share portions of the data or business logic with a public blockchain without risking exposure of private business data.
Implementing a hybrid model for security mitigates risks associated with data breaches and nefarious actors as sensitive data can be secured at the business level and the business can selectively choose what data to distribute and to whom. During the verification process the data payload from every transaction never leaves the business’s blockchain nor is it exposed in any way unless the business explicitly wishes. Instead, the proof of the data is sent for decentralized verification leaving the private and proprietary data to be secured by the business. This type of data segregation allows the system to be GDPR and CCPA compatible and safeguards sensitive data such as personal identifiable information (PII) from end to end.
Measurable Security of Multiple Blockchains
With the use of Interchain, Dragonchain can leverage the hash power of multiple public blockchains (e.g. Bitcoin and Ethereum) for what we call “measurable security”. To quantify the amount of security afforded to each individual transaction, Dragonchain pioneered the definition of Transaction Security Value (TSV). This value shows, in real-time, how many dollars ($USD) of energy consumption has been used to secure a transaction from the moment the transaction is posted. Starting in the millions of dollars, the value continually increases over time as more and more Bitcoin and Ethereum blocks are added to their respective chains.
Quantum Encryption
Dragonchain offers quantum encryption and signing capabilities integrated at the core of our hybrid blockchain architecture. With our quantum encryption capabilities, businesses can ensure that their data is secured at rest on their private blockchain, when being validated on public blockchains, and when shared with partners.
Behavior Systems
Unique to Dragonchain is our use of patented behavior systems algorithms -- again pioneered at Dragonchain -- to address security and counter fraud. We have spearheaded patterns and processes for businesses to incentivize human behavior to improve system security that goes beyond code to leverage measured human behavior.
Dragonchain’s Blockchain Scalability
Outside of security, scalability is an important capability for the business to consider when choosing a blockchain platform. Businesses must be flexible enough to scale operations up or down as needed and they must be able to meet existing transaction volume. Unfortunately, most blockchain platforms in use today still struggle to scale.
Scalability Amongst Other Platforms
Most blockchain platforms in use today approach scalability through hardware. Blockchain networks that rely on specialized hardware are unable to scale for the long term and will not be able to handle Enterprise level transaction volume. These platforms will be adversely affected by higher network congestion along with increased fees with the addition of expanding business systems, whether from the same business or those of business partners. When this happens, the business will find that hardware integrated for blockchain implementation is now obsolete and additional hardware must be obtained at increased expense. Additionally, as technology advancements continue, what was once the latest and greatest quickly becomes obsolete, requiring expensive new infrastructure build-out in an ever-changing environment. And, if the business encounters a sudden downturn in operations, they will waste resources maintaining expensive hardware that is sitting idle.
Dragonchain takes a 3-dimensional approach to scaling blockchain networks.
Dragonchain’s Scalable Architecture
Dragonchain’s patented architecture employs a series of interwoven blockchains that scale horizontally as well as vertically. Every business blockchain interops with Dragonchain’s verification platform called Dragon Net. Through the use of our patented Interchain technology, any traditional business system or blockchain can connect to any other business system or blockchain to ledger transactions or execute smart contract logic.
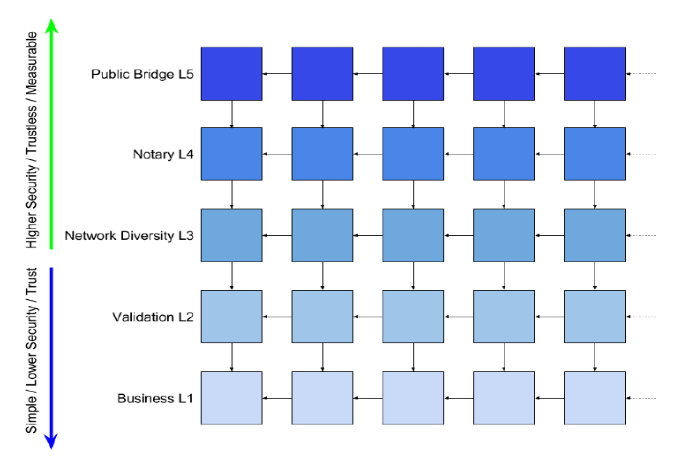
Dragon Net is scalable by design wherein every business and verification node has its own independent blockchain. The Dragon Net platform is best described as a "blockchain of blockchains," and provides five levels of consensus known as Context-Based Verification. As the verification level increases for a block, security increases, and risk decreases.
Level 1 Business Verification (Approval)
Each business operates its own private blockchain(s) where it can privately process transactions and secure data on-chain.
Level 2 Enterprise Verification (Validation)
Defined by the Enterprise, Level 2 validation nodes check blocks for individual transaction validity in form, signature, and required data elements. Every business transaction is validated by three independent decentralized Level 2 validation nodes.
Level 3 Network Diversity Verification
All Level 3 nodes are independent and decentralized as well. This verification context will ensure that the Level 2 validations of transactions are coming from a sufficiently diverse set of distributed sources. It also provides control and measurement of network effect and provides distributed security as an attacker would be required to attack multiple blockchain systems, businesses, and data centers to tamper with existing data.
Level 4 Decentralized Independent Verification (Notary)
All decentralized Level 4 nodes provide notary verification to the consensus process. Hosted by an independent individual or entity with a known and verified identity. Level 4 nodes cryptographically sign any Level 3 verification blocks that it receives. This function allows the Level 4 node to automatically act as an independent witness to Level 3 verifications.
Level 5 Public Verification (Public Checkpoint)
A Level 5 node provides an interface and bridge for individual business blockchains to interact with one or more public blockchain networks (e.g. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, etc.). The system provides a human-readable report as well as API access to this capability.
This multidimensional scaling approach allows businesses to add or remove systems and activity without affecting Dragon Net and without affecting their own business systems.
Dragonchain’s Economic Scalability
In addition to technical scalability, it is critical to economically scale blockchain networks to limit fee volatility.
To maintain a deterministic fee structure, Dragonchain applies a scarcity model based on the passage of time. On the Dragonchain platform, TIME is calculated as the number of Dragons in a single address multiplied by the number of days held in that address. (1 DRGN * 3 Days = 3 TIME) TIME can be considered a reputation or loyalty measure and determines the owner’s access to features within the Dragonchain ecosystem. TIME is staked by users against every verification node and determines how much of the transaction fees from every business transaction block are awarded to all competing verification nodes.
TIME also dictates the transaction fee itself for business nodes. TIME is staked against a business node to configure and lock a deterministic fee level for every transaction and ensure that the business is independent of other networks on the platform and will not see any increase in network fees or congestion if transactions from other businesses increase.
Scaled Deployment
An important feature of the Dragonchain platform is the ability for businesses to use commodity hardware, operating systems, and platforms. Well-known and widely used commodity hardware solutions such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Intel, and AMD give businesses the flexibility to deploy to any environment they choose. Open source and standardized systems, such as Linux, Unix, Docker, Kubernetes, and other projects provide the biggest pool of knowledgeable users to build and operate business systems. Dragonchain offers an environment where developers can flexibly deploy and scale smart contracts and blockchain-based systems using resources and tools with which they are already familiar.
To prove the functionality of our scalability model, in January 2020 Dragonchain held a 24-hour live demonstration in which a quarter of a billion (250 million+) transactions were executed fully on an operational network. Every single transaction on Dragonchain was immediately decentralized through 5 levels of Dragon Net and then secured with combined measurable proof on Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, and Binance Chain, via Interchain. This means that every single transaction is secured by, and traceable to these networks.
The demonstration was of a single business system, and any user could scale this further, by running multiple systems simultaneously. We met our goals for the event and demonstrated a consistent capacity greater than that of Visa over an extended time period on an operational system with real data.
Why is scalability important?
To truly take advantage of blockchain technology securing data on-chain needs to be ubiquitous. Dragonchain’s scalability makes it possible for businesses to record, on-chain, every substantive business event (e.g. every time a user does something important or every time there is sensor data). Businesses can “roll back the clock” and provide independent measurable proof of the true state of all data points at any time in the past. This includes the ability to provide a deep analysis of the complete historical system state with extreme confidence.
Dragonchain’s Decentralized Blockchain Platform
Most blockchain platforms in operation today do not understand that businesses can not put sensitive data on-chain for all to see. For this reason, Dragonchain takes a hybrid approach to decentralization.
As mentioned earlier, every blockchain within the platform is independent, including the business’s blockchain. This independence allows business transactions to be usable in near real-time. Every Level 1 business blockchain forms a block every 5 seconds as long as data presents itself. Each block is then verified and validated within seconds by a set of decentralized nodes within Dragon Net. Finally, full decentralization occurs to public or otherwise external chains (e.g. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Binance Smart Chain) within a few minutes or hours based on the public chain and its network. These nodes scale the system by aggregating multiple blocks into a single Interchain transaction on a cadence. Meanwhile, the Level 1 business blockchain is unaffected by the rest of the verification process.
Dragonchain also uses decentralization as a security feature. Every node on the interoperable hybrid blockchain platform is its own decentralized blockchain and as such is exponentially more resilient to a 51% attack. Additionally, we leverage the enormous security of Bitcoin and Ethereum for measurable proof without bogging down the Dragon Net network or the business’s blockchain with unscalable PoW public chains.
What does this mean?
To maliciously alter business data a nefarious actor would have to compromise the business’s blockchain, the entire network of independent distributed decentralized verification blockchains (Levels 2-4), and all public networks connected via Interchain (e.g. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Binance Smart Chain).
As you can see, when it comes to the blockchain trilemma Dragonchain does not compromise. Dragonchain is the only platform capable of scaling to today’s centralized global volume while still offering decentralized verification with measurable proof and unmatched security where it matters to a business.
Contact us to get started today!